What are The Steps of the Development Process For A Software Project?
Table Of Content
Published Date :
08 Apr 2025
Every app, website, or system you use started as an idea. But turning that idea into a fully functional product? That takes a structured process. Whether it’s the AI behind your chatbot, the cloud apps running your business, or the IoT devices making your home smarter, every piece of software follows a structured process before it ever reaches you.
With advanced technologies like AI, Cloud Computing, and IoT, the landscape of software development has completely changed. Every business or app owner builds software that scales according to business or user needs.
Software development isn’t just about writing code anymore, businesses are shifting their focus to build apps that are intelligent and scalable.
But no matter how advanced the tech gets, the core process to develop the software stays the same. It includes a set of steps from planning, designing, building, testing, and improving. Skip a step, and you don’t just get a few glitches, you get a full-blown disaster.
In this blog, we’ll break down the software development process and what it takes to build a successful project.
Build Better Software with a Proven Process!
From planning to deployment, we follow a structured approach tailored to your goals.
What is a Software Development Process?
The software development process is a structured approach that software teams follow to build applications and systems. It consists of a series of steps from planning and design to coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance, ensuring the project stays organized and on track.
A well-defined process helps teams collaborate efficiently, reduce risks, and deliver high-quality software that meets both business and user needs. While different methodologies like Agile, Waterfall, and DevOps influence how these steps are executed, the fundamental stages remain the same:
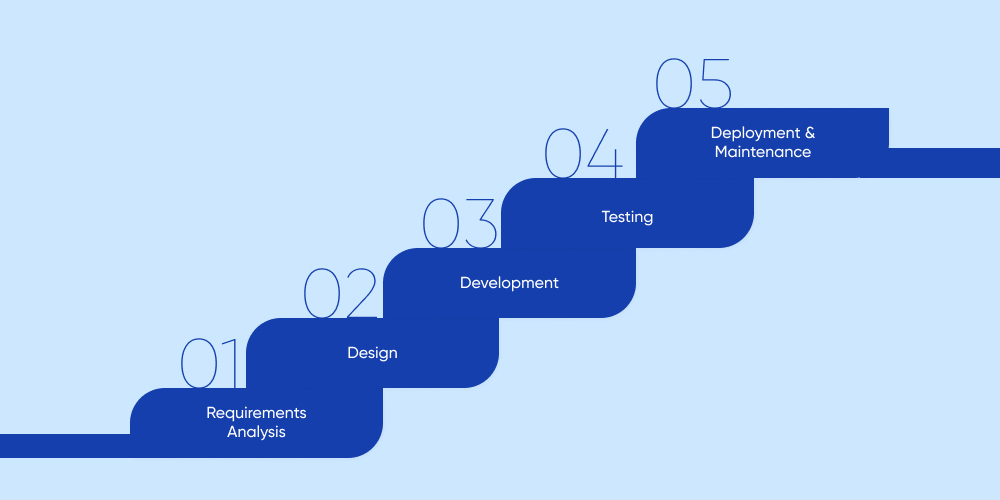
- Requirements Analysis
- Design
- Development
- Testing
- Deployment & Maintenance
Why is the Software Development Process Important?
The software development process is essential for delivering reliable, high-quality software. It provides a structured framework that ensures efficiency, minimizes errors, and maintains consistency throughout the development lifecycle. Without a well-defined process, software projects can face cost overruns, missed deadlines, security vulnerabilities, and poor performance.
Key Benefits of a Structured Development Process
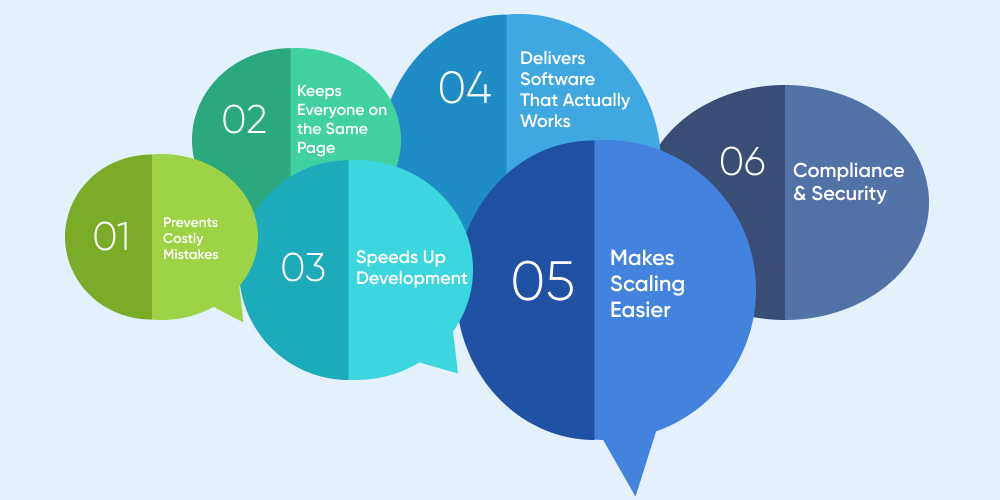
- Prevents Costly Mistakes: Skipping steps or rushing can lead to security flaws, performance issues, and massive rework. A step-by-step approach helps identify and address potential issues early, reducing the risk of critical failures post-deployment.
- Keeps Everyone on the Same Page: Developers, testers, designers, and stakeholders all work better with a clear roadmap. Clear planning and defined roles ensure that time, budget, and development resources are optimized effectively.
- Speeds Up Development: Having a defined process actually makes things faster. Less backtracking, fewer bottlenecks, more efficiency.
- Delivers Software That Actually Works: No one wants a buggy, unreliable app. A proper development process ensures thorough testing, so what gets delivered is functional, secure, and user-friendly. Rigorous testing at each stage of development ensures the software meets functional, security, and performance requirements.
- Makes Scaling Easier: Want to add new features later? A well-structured codebase makes updates and expansions a breeze.
- Compliance & Security: Adhering to industry standards and best practices helps maintain regulatory compliance and enhances software security.
Full-Cycle Development Backed by Modern Tech!
We use AI, cloud, and DevOps to streamline your software journey from start to scale.
Key Steps in the Software Development Process
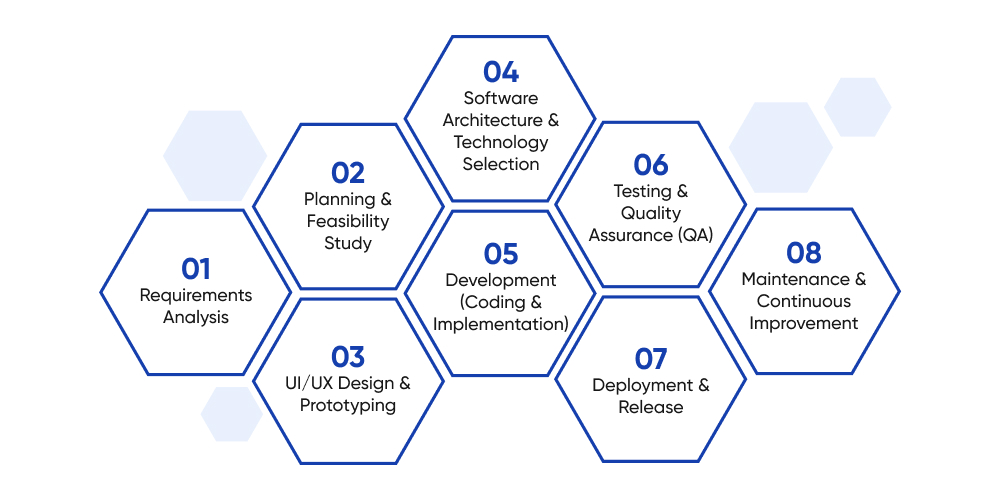
1. Requirements Analysis
Before writing a single line of code, you need a clear roadmap. That’s where requirements analysis comes in. This step is all about defining what the software needs to do, who it’s for, and what constraints or challenges might come up.
Developers, project managers, and stakeholders collaborate to gather business needs, user expectations, and technical requirements.
This phase typically involves:
- Stakeholder meetings to understand business goals
- User research to define pain points and expectations
- Technical feasibility analysis to identify potential roadblocks
- Creating requirement documents (functional and non-functional)
A solid requirements analysis prevents costly changes later. It ensures everyone is aligned before development begins, because fixing a mistake in the planning phase is far easier (and cheaper) than rewriting half the codebase later.
2. Planning & Feasibility Study
Not every idea makes it to development, some fail before they even start. This phase determines whether the project is viable before investing time and resources.
- Feasibility Analysis: Can the project be realistically built with available technology, budget, and time? This covers technical, financial, and operational feasibility.
- Market Research: Is there a demand for the product? Competitive analysis helps gauge its potential success.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying technical, financial, and operational risks early helps in planning mitigation strategies.
- Project Roadmap: Defines the project scope, timeline, resource allocation, and expected outcomes.
This phase ensures that the project is strategically and financially sound before moving forward. Without it, teams risk wasting resources on something impractical or unsustainable.
3. UI/UX Design & Prototyping
At this stage, the focus shifts from “what the software does” to “how users interact with it.” A well-designed interface can make or break a product. If users struggle to navigate it, even the most powerful features won’t matter.
Key Steps in This Phase:
- User Research: Who’s using the software? What do they need? What frustrates them? Answering these questions ensures the design is user-centric.
- Wireframing: This helps map out the layout and structure before diving into detailed design.
- Prototyping: An interactive mockup that mimics real user interactions. This lets teams gather feedback before a single line of code is written.
- UI Design: Finalizing the look and feel like colors, fonts, buttons, and overall branding to create a polished, cohesive experience.
- Usability Testing: Real users, real feedback. This step uncovers pain points so adjustments can be made early.
4. Software Architecture & Technology Selection
This step lays the foundation for the entire project. Choosing the right architecture and tech stack determines how scalable, secure, and maintainable the software will be. A poor decision here can lead to performance bottlenecks, security risks, or a system that’s impossible to scale.
Key Decisions in This Phase:
- Architecture Design: Will it be monolithic, microservices, serverless, or event-driven? The choice depends on factors like scalability, flexibility, and business needs.
- Tech Stack Selection: It includes picking the right programming languages, frameworks, and databases. For example, Python and Django for AI-driven apps, or React and Node.js for web applications.
Cloud vs. On-Premises: Cloud solutions (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) offer scalability, while on-premises solutions provide full control. Hybrid models are also an option. - Security & Compliance: Implementing security best practices and ensuring compliance with industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Integration Strategy: How will the system connect with third-party tools, APIs, or existing infrastructure?
Your Idea, Delivered with Precision!
Partner with a team that brings structure, speed, and strategy to every software build.
5. Development (Coding & Implementation)
This is where the actual software takes shape. Developers start writing code based on the architecture and design decisions made in the previous steps. A structured approach ensures the software is scalable, maintainable, and free of unnecessary complexity.
Key Aspects of the Development Phase:
- Backend Development: Handles the core logic, databases, and server-side functionality. Languages like Python, ASP.Net, Java, and Node.js are common choices.
- Frontend Development: Focuses on user-facing elements, ensuring a smooth and responsive experience. Technologies like React, Angular, or Vue.js are often used.
- API Development & Integrations: Connecting different systems, third-party services, and databases to enable seamless functionality. RESTful APIs, GraphQL, and WebSockets are common approaches.
- Version Control & CI/CD Pipelines: Using Git for code management and CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) to automate testing and deployment.
- Coding Best Practices: Writing clean, modular, and well-documented code to ensure maintainability and easy debugging.
This phase is usually iterative, especially in Agile environments, where features are built and tested in cycles rather than all at once.
6. Testing & Quality Assurance (QA)
Once the code is written, it needs to be tested rigorously. Bugs, security flaws, and performance issues can break a product if left unchecked. This phase ensures the software works as expected, meets user requirements, and is free from critical issues before deployment.
Types of Software Testing:
- Unit Testing: Developers test individual components or modules to ensure they function correctly.
- Integration Testing: Ensures different parts of the system (APIs, databases, third-party services) work together seamlessly.
- Functional Testing: Validates that the software meets business and user requirements.
- Performance Testing: Measures speed, scalability, and stability under different workloads.
- Security Testing: Identifies vulnerabilities and ensures data protection.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Real users test the software to confirm it meets their needs before final release.
Automation vs. Manual Testing
Testing can be done manually or automated using tools like Selenium, Cypress, and JUnit. Automated testing speeds up the process and ensures consistency, while manual testing helps identify usability and edge-case issues.
A strong QA process reduces post-launch failures, improves user experience, and saves time and costs in the long run. Skipping or rushing this phase is never an option.
7. Deployment & Release
Once the software passes all quality checks, it's time to deploy it for real-world use. This step involves setting up the production environment, configuring servers, and ensuring a smooth transition from development to live operations.
Deployment Approaches
- Big Bang Deployment: The entire software is released at once. Works best for smaller projects with minimal dependencies.
- Phased Rollout: Released gradually to a subset of users before full-scale deployment. Helps identify and fix issues early.
- Blue-Green Deployment: Two identical environments (blue and green) are used. The new version is deployed to one, and traffic is switched once validated. Ensures zero downtime.
- Canary Release: A small percentage of users get access first, and if everything works fine, it's expanded. Great for risk mitigation.
Post-Deployment Checklist
- Monitor system performance and error logs.
- Check for security vulnerabilities.
- Collect user feedback and fix any immediate issues.
- Ensure rollback plans are in place in case of failures.
8. Maintenance & Continuous Improvement
Software development doesn’t stop after deployment. Once the product is live, it requires ongoing maintenance to ensure performance, security, and user satisfaction. This phase involves fixing bugs, optimizing performance, and rolling out updates based on user feedback and evolving business needs.
Key Aspects of Maintenance
- Bug Fixes: Even with rigorous testing, real-world usage can expose issues. Quick patches keep the system stable.
- Performance Optimization: Monitoring and fine-tuning code, database queries, and infrastructure to maintain efficiency.
- Security Updates: Addressing vulnerabilities and applying security patches to protect against cyber threats.
- Feature Enhancements: Adding new functionalities and improving existing ones based on user feedback.
- Scalability Improvements: Upgrading infrastructure and optimizing architecture to handle growing user loads.
Continuous Improvement
Software isn’t static. Technologies evolve, user expectations shift, and business goals change. Adopting a continuous improvement mindset through DevOps practices, automated monitoring, and iterative updates ensures that the software remains relevant and competitive over time.
How DITS Can Help?
At DITS, we approach every project with a tailored strategy, ensuring that your software aligns perfectly with your business goals. Whether you're developing a new application, modernizing an existing system, or optimizing performance, we provide end-to-end support to keep everything on track.
Our team specializes in full-cycle development, handling everything from initial planning and architecture to deployment and long-term maintenance. We follow agile methodologies to ensure flexibility and adaptability, allowing us to respond quickly to changes and new requirements. Quality is at the core of everything we do rigorous testing, security best practices, and performance optimizations ensure that your software is reliable, secure, and built to scale.
Technology is constantly evolving, and we make sure our clients stay ahead. We develop AI-driven solutions, integrate cloud-native architectures, and DevOps automation to enhance efficiency and future-proof your software. Whether you need custom software development Canada, cloud migration, automated testing, or system modernization, our expertise covers a wide range of digital transformation needs.
Conclusion
The software development process isn’t just a series of steps, it’s the foundation for building reliable, scalable, and high-performing applications. From initial planning to continuous improvement, each phase plays a critical role in ensuring the final product meets both business objectives and user expectations.
A well-structured development process minimizes risks, optimizes resources, and ensures a smooth path from idea to execution. Choosing the right approach, AI tools for software development, and development partner can make all the difference in delivering a solution that stands the test of time.
At DITS, we bring expertise, innovation, and a commitment to quality at every stage of development. Whether you're launching a new product or refining an existing one, we ensure your software is built for success. Let’s turn your vision into reality.
FAQs
1. What is the software development process?
The software development process is a structured approach to designing, developing, QA testing, and maintaining software. It ensures that software is built efficiently, meets requirements, and is scalable for future updates.
2. Why is the software development process important?
A well-defined process helps teams stay organized, reduces development risks, improves collaboration, and ensures high-quality software. It also minimizes errors and ensures the final product aligns with business and user needs.
3. What are the main steps in software development?
The process typically includes:
- Planning & Feasibility Study
- UI/UX Design & Prototyping
- Software Architecture & Technology Selection
- Development (Coding & Implementation)
- Testing & Quality Assurance
- Deployment & Release
- Maintenance & Continuous Improvement
4. What are the different software development methodologies?
Common methodologies include:
- Agile: Iterative development with continuous feedback.
- Waterfall: A linear, sequential approach.
- DevOps: Focuses on collaboration between development and IT operations.
- Scrum: A subset of Agile that organizes work in sprints.
5. How long does software development take?
It depends on project complexity, scope, and methodology. Simple apps may take a few months, while large-scale enterprise solutions can take a year or more.
6. How do I choose the right technology for my project?
The choice depends on project requirements, scalability needs, budget, and development expertise. A software development partner like DITS can help assess the best tech stack for your solution.
7. How much does software development cost?
Costs vary based on features, complexity, team size, and location. A small app may cost a few thousand dollars, while enterprise-grade software can run into millions.
8. How does DITS help in software development?
DITS offers end-to-end software development services, from planning to deployment. Our expertise ensures efficient development, quality assurance, and long-term support to keep your software running smoothly.

Dinesh Thakur
21+ years of IT software development experience in different domains like Business Automation, Healthcare, Retail, Workflow automation, Transportation and logistics, Compliance, Risk Mitigation, POS, etc. Hands-on experience in dealing with overseas clients and providing them with an apt solution to their business needs.
Recent Posts

Discover how bespoke MVP development services help Canadian companies reduce product risk, validate ideas faster, and build scalable products with confidence.

Quality management system software helps small businesses proactively manage compliance, reduce operational risk, improve audit readiness, and build scalable, resilient quality processes across regulated environments.

Simplify stock control with inventory management software designed for small manufacturing businesses. Reduce errors and improve planning.