5 R's Of Application Modernization Strategy Every Business Should Know
Table Of Content
Published Date :
21 May 2025
Most legacy apps weren’t built for how businesses operate today. They were built long before cloud and mobile became the norm. But now? Your business moves fast and your users expect faster. And your competitors are already moving fast with cloud-native platforms, sleek UX, and AI-driven processes.
That leaves your old systems acting more like a liability than an asset. They slow your teams down, frustrate users, and rack up maintenance costs.
Many organizations know they need to modernize, but here’s where most get stuck: How do you do it without impacting business operations or blowing your budget?
Do you need to rebuild from scratch, refactor, or replace? Or just keep patching it up and hoping for the best?
For decision makers, the challenge is clear. The answer lies in a strategic process that evaluates each application and applies the right approach. This approach is known as the 5 R’s of application modernization. These five R's provide a practical way to update legacy systems while keeping your business running smoothly.
In this article, we’ll break down each strategy to help you modernize with confidence, minimize risk, and get the most value from your applications.
What is Application Modernization?
Application modernization is the process of updating legacy software or apps to align with current business needs, technologies, and user expectations. Rather than eliminating the application entirely, the application modernization process focuses on improving it. This can involve rearchitecting, refactoring, rehosting, or replacing specific components.
Ready to Modernize Your Applications?
Discover which of the 5 R’s is right for your business. Get expert guidance tailored to your tech stack and goals.
Types of Legacy Application Modernization
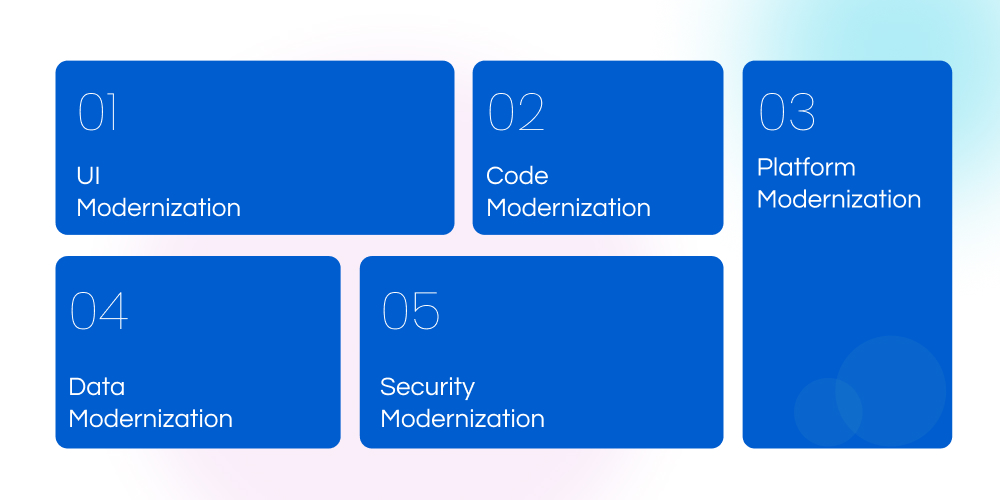
Let’s break down the five common types of modernization:
1. UI Modernization
Let’s start with what your users actually see.
A clunky, outdated interface can kill user engagement faster than a loading spinner on a slow Wi-Fi. UI modernization is all about revamping the front-end and giving your app a cleaner, faster, more intuitive design.
You modernize the UI when:
- Users complain about usability or visual appeal
- It feels like using software from 2012
- You want better mobile responsiveness
2. Code Modernization
Code modernization means rewriting (or at least refactoring) the codebase to make it more efficient, scalable, and readable. It could be moving from a mess of jQuery to React. Or refactoring legacy Java code into clean microservices.
Why it matters:
- Modern code is easier to maintain
- Future-proofing against outdated tech stacks
- Better performance, lower bugs, happier devs
3. Platform Modernization
Platform modernization means moving away from rigid, on-prem setups or outdated hosting models to something more flexible like cloud, containers, or serverless architectures.
Common upgrades include:
- Migrating to AWS, Azure, GCP
- Moving from VMs to Kubernetes
- Moving from old monolith for microservices
4. Data Modernization
Data is useless if it’s buried in silos or locked in legacy formats. Data modernization is about transforming how your business handles, stores, and uses data. It means real-time access, cloud-native databases, better integrations, and analytics that don’t require a PhD to interpret.
In simple terms? It’s the difference between hunting for spreadsheets and having insights on tap.
Why it’s worth doing:
- Real-time decision-making
- Easier compliance and governance
If your data lives in six places and none of them talk to each other, this is your starting point.
5. Security Modernization
Old systems were built for a world that no longer exists. Security modernization brings in practices like:
- Zero trust architecture
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- End-to-end encryption
- Continuous monitoring
If your app handles sensitive data like customer info, financials, medical records or more, security modernization is the must.
Also Read: How to Modernize Legacy Applications
What Technologies Require Modernization?
Not every part of your tech stack needs a complete overhaul. But some technologies tend to slow you down, limit your growth, or just don’t go along with the modern architecture your applications require. Knowing where to focus your efforts makes all the difference.
1. Legacy applications often top this list. These old systems are built on platforms like COBOL, VB6 or classic ASP. They usually live on-premise, lack cloud compatibility, and can’t easily support new user experiences, especially mobile.
2. Databases are another common bottleneck. Monolithic databases aren’t easy to scale or can’t handle real-time data. Modern applications demand databases that are flexible, scalable, and ready to serve analytics on demand.
3. Maintaining physical servers or data centers might have made sense years ago, but these days, on-premise setups limit how fast you can scale and often pose security challenges that cloud platforms handle more gracefully.
4. If your systems are tied together with fragile, hard-coded connections or legacy middleware, a single glitch can bring everything down. Modern architectures prefer APIs and microservices that talk seamlessly and keep your systems flexible.
5. Outdated frontends that only work on desktops or aren’t mobile-friendly frustrate users and kill engagement. Modernizing your UI means better performance, personalization, and accessibility, which directly impacts satisfaction and loyalty.
6. If your approach is reactive, missing encryption or multifactor authentication, or not compliant with today’s regulations, you’re compromising the critical data.
Modernization Starts With a Clear Plan!
Fill out the form and get a custom roadmap aligned with your modernization goals using the 5 R’s framework.
The 5 R’s of Application Modernization
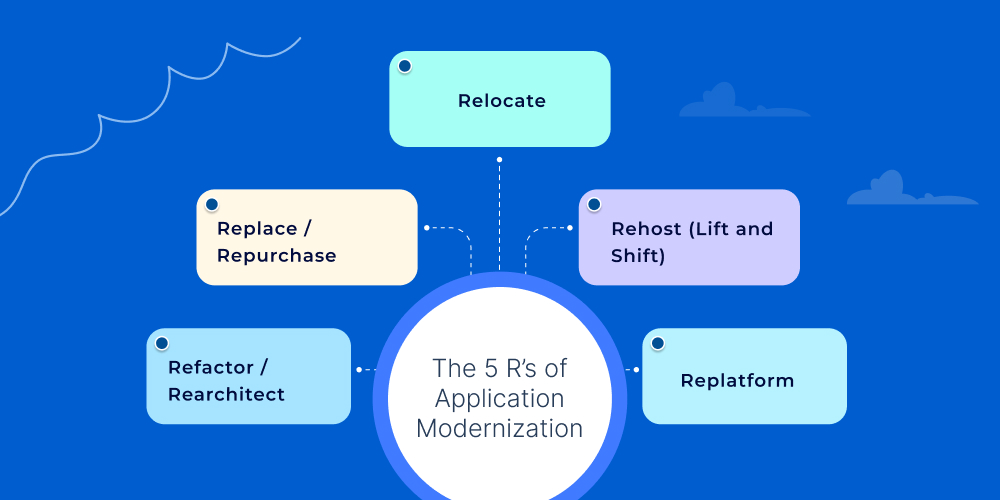
The 5 R’s provide a practical framework to evaluate your applications and decide how best to evolve them to meet today’s performance, scalability, and agility demands.
1. Refactor / Rearchitect
This involves restructuring and optimizing the existing codebase without changing its core functionality. It often includes breaking monolithic applications into microservices or migrating to newer programming frameworks.
Who it’s for
- Organizations with valuable but outdated codebases
- Systems that need long-term scalability or improved architecture
Who it’s not for
- Businesses seeking rapid results
- Applications with uncertain future use
Pros and Cons of Refactor / Rearchitect
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
2. Replatform
This approach moves an application to a new platform (typically cloud) with minimal changes to the core code. It may involve adopting containers, managed databases, or platform services.
Who it’s for
- Stable applications facing platform obsolescence
- Organizations aiming for cost or performance gains
Who it’s not for
- Systems with deep technical debt
- Applications that won't benefit from new infrastructure
Pros and Cons of Replatform
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
3. Rehost (Lift and Shift)
Rehosting simply relocates the application to the cloud without modifying its architecture or code. It’s often used for quick cloud migrations.
Who it’s for
- Organizations with tight timelines or budgets
- Teams looking to reduce infrastructure costs fast
Who it’s not for
- Performance-critical applications
- Legacy systems with architecture challenges
Pros and Cons of Rehost (Lift and Shift)
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
4. Replace / Repurchase
In this model, the legacy application is replaced entirely with a commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) or Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solution.
Who it’s for
- Organizations where the application isn’t a competitive differentiator
- Functions like HR, finance, or CRM that align well with SaaS models
Who it’s not for
- Heavily customized or industry-specific software
- Systems requiring full control over features and data
Pros and Cons of Replace / Repurchase
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
5. Relocate
Relocate involves moving applications between environments typically from one cloud to another without modifying their code or architecture.
Who it’s for
- Organizations switching cloud providers
- Workloads already containerized or virtualized
Who it’s not for
- Systems hardwired to specific infrastructure
- Applications with significant modernization needs
Pros and Cons of Relocate
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Also Read: Top 10 Benefits of Legacy Application Modernization
Here’s How to Find the Best-Fit ‘R’ for Your Application
| Strategy | Description | Pros | Cons | Best Fit For |
| Refactor | Code-level changes to improve structure | Scalable, modern, future-proof | High effort and cost | Apps with long-term value and growth potential |
| Replatform | Move to new platform with tweaks | Enables cloud-native tools | Retains legacy codebase | Stable apps needing cloud benefits |
| Rehost | Lift-and-shift to cloud | Quick and low-cost migration | No architectural improvement | Cost-driven or transitional strategies |
| Replace | Move to SaaS or COTS | Low maintenance, quick ROI | Limited flexibility, vendor lock-in | Commodity apps (HR, payroll, CRM) |
| Relocate | Move between cloud environments | Minimal effort, infrastructure swap | Doesn’t solve core legacy issues | Cloud-to-cloud or data sovereignty needs |
Not Sure Which Modernization Path to Take?
Rehost, Refactor, Rearchitect—let’s help you choose the best strategy for your applications.
Beyond the Big 5: Non-Migration R’s You Shouldn’t Overlook
Sometimes, the smartest strategy is to leave things right where they are or let them go entirely. That’s where these two often-overlooked R’s come in:
Retain
Keep it as-is, for now.
Sometimes an application is doing its job just fine. Maybe it’s stable, has no performance issues, and doesn’t need the bells and whistles of modern architecture. Or maybe modernizing it would be more hassle than it’s worth.
Who it’s for:
- Apps with low business value but high stability
- Legacy systems that don’t justify the investment
- Components that will eventually be phased out
Who it’s not for:
- Customer-facing apps falling behind in UX or performance
- Systems with security or compliance risks
- Apps blocking broader modernization efforts
Pros and Cons of Retain
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Retire
Every organization has them: forgotten tools, duplicate systems, or apps that were built for a need that no longer exists. If it’s not being used (or shouldn’t be), retiring it frees up resources and reduces risk.
Who it’s for:
- Unused or redundant applications
- Legacy systems that no longer align with business needs
- Apps draining resources without delivering ROI
Who it’s not for:
- Apps still serving critical workflows
- Systems with hidden dependencies
- Anything under active contract or compliance scrutiny
Pros and Cons of Retire
| Pros | Cons |
|
|
Also Read: Top 7 Signs That Your Legacy System Needs Modernization
Which Application Modernization Approach Is Best?
There’s no universal “best” R. The right modernization approach depends on your business priorities, your tech reality, and your team’s capacity to change. Choosing without thinking it through? That’s how teams end up spending six figures to modernize an app no one even uses.
Here’s how to narrow it down.
Ask these to the people who live with the app every day:
Is this app business-critical?
If it goes down, does the business stop? If yes, tread carefully. You might need a phased modernization, not a full replacement.
Can we afford downtime?
Rehosting might be fast but if even a few hours offline would cause chaos, you’ll need a solid migration strategy with fallback options.
Is the existing codebase maintainable?
If your devs cry every time they open it, refactoring might be necessary. But if it’s clean and modular, a simple replatform might do.
Are we chasing short-term fixes or long-term value?
Need speed? Rehost or replatform. Want flexibility, scalability, and future-proofing? Rearchitect or replace might be worth the extra effort.
What’s our in-house capability right now?
If your team isn’t ready for a full-on rearchitecture, forcing it will only burn time and morale. Pick an approach your current resources can handle or plan to bring in help.
Don’t Let Legacy Systems Hold You Back!
Fill out the form to explore how application modernization can reduce costs and improve performance.
How the 5 R’s Work Together?
In reality, most organizations use a mix of modernization approaches because different apps have different lifespans, roles, and pain points. One app gets refactored, another gets rehosted and a third is quietly replaced with a SaaS tool that just works better. And that’s exactly how it should be.
Start With the App Portfolio, Not the ‘R’
Before deciding how to modernize, take a step back and look at what’s actually in your application stack:
- Which apps are critical to business continuity?
- Which ones are hanging on by a thread?
- What’s costing more than it’s worth?
- Are there overlaps or unused systems?
One Strategy Doesn’t Fit All
Here’s a real-world scenario:
- You refactor your custom order management system to integrate AI-driven demand forecasting.
- You rehost your legacy HR platform to the cloud to reduce infrastructure overhead.
- You replace your outdated ticketing tool with a modern SaaS helpdesk.
The Smarter Approach: Mix, Match, and Modernize
Trying to use the same strategy across your entire stack? Modernization works best when it’s tailored to context. Use the R’s like tools in a kit, choose based on what fixes the problem, not what sounds most impressive.
The Role of Cloud Technology in Modernization
Whether you're refactoring an app to go cloud-native or just lifting and shifting to buy time, the cloud gives your modernization efforts flexibility, scalability, and speed.
How Cloud Supports Each of the 5 R’s
- Rehost: Migrating applications “as-is” to cloud infrastructure (IaaS).
- Replatform: Making minimal changes to leverage managed cloud services such as databases, storage, or container orchestration.
- Refactor: Redesigning applications to fully leverage cloud-native architectures, including microservices and serverless functions.
- Replace: Substituting legacy applications with modern SaaS alternatives.
- Relocate: Moving entire workloads or environments to different cloud regions or providers.
How DITS Supports Your Application Modernization Journey
At Ditstek Innovations (DITS), we don’t believe in one-size-fits-all solutions especially when it comes to modernization. Every business is working with a different mix of legacy systems, priorities, and technical debt. That’s why we take a portfolio-driven approach.
We start by assessing what’s working, what’s holding you back, and where modernization will actually move the needle. Whether that means refactoring a business-critical app, rehosting for a faster cloud migration, or replacing outdated tools with a modern SaaS. Our team helps you choose the right “R” for each application.
Our engineers specialize in:
- Cloud-native development
- Legacy-to-modern migration
- Microservices and containerization
- DevOps automation
- UI/UX redesigns
- Secure data migration
- API-driven integrations
More importantly, we partner with you through the entire lifecycle from planning and roadmapping to implementation, testing, and continuous optimization.
Let’s make yours smarter, faster, and ready for what’s next.
Want to explore what modernization could look like for your business? Let’s connect.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is application modernization?
Application modernization is the process of updating legacy software systems to align with modern business needs, technologies, and user expectations. This can involve migrating to the cloud, refactoring code, improving UI/UX, or even replacing apps with SaaS alternatives.
2. What are the 5 R’s of application modernization?
The core 5 R’s are:
- Refactor/ Re-architect: Restructure code to improve performance and scalability.
- Replatform: Move to a new platform (often cloud) without major code changes.
- Rehost: “Lift and shift” the application as-is to new infrastructure.
- Replace/ Repurchase: Swap out legacy apps for SaaS or COTS solutions.
- Relocate: Move apps to a different environment, typically within cloud infrastructures.
3. Are there more than 5 R’s?
Yes. While the "5 R's" are core strategies, two additional approaches: Retain (keep as-is) and Retire (decommission) round out a complete modernization strategy. These are non-migration options, best for apps that are stable or no longer needed.
4. Which modernization strategy is best?
It depends on your business goals, application complexity, urgency, and available resources. Often, a mix of strategies works best. Assess each app’s role, technical state, and ROI potential before deciding.
5. How do I know if an application should be modernized?
Start by asking:
- Is this application business-critical?
- Is it difficult to maintain or scale?
- Does it limit integration, performance, or security?
- Can it support future business needs?
If the answer is “yes” to several, it’s likely a strong candidate for modernization.
6. What role does the cloud play in modernization?
Cloud allows for better scalability, agility, and access to modern services like AI, data analytics, and container orchestration. Most modernization strategies involve at least some degree of cloud migration.

Dinesh Thakur
21+ years of IT software development experience in different domains like Business Automation, Healthcare, Retail, Workflow automation, Transportation and logistics, Compliance, Risk Mitigation, POS, etc. Hands-on experience in dealing with overseas clients and providing them with an apt solution to their business needs.
Recent Posts

Digital transformation in healthcare streamlines operations, reduces administrative waste, strengthens revenue cycles, and enables data-driven decisions that support sustainable cost control and improved care delivery.

Reduce operational risks and errors by replacing manual, spreadsheet-based processes with dispatch management software.

Discover how bespoke MVP development services help Canadian companies reduce product risk, validate ideas faster, and build scalable products with confidence.